List of Figures
 |
Figure 1:
The push and pull migration model applied to Portugal. |
 |
Figure 2:
Map of European net migration between 2000 and 2006, encompassing the expansion of the EU in 2004 (Source: GISCO, 2009). |
 |
Figure 3:
Map showing expected relative population change in the EU from 2004 – 2031. Note the gaps in data and also the varying spatial scales of resolution, especially in the UK and France compared with other countries (Source: GISCO, 2009). |
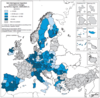 |
Figure 4:
Map showing net projected cumulative changes in international migration for selected countries. Note the major gaps in data, representing some of the major source and destination countries for intra-European migration flows (Source: GISCO, 2009). |
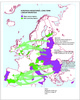 |
Figure 5:
Map showing expected primary flow directions of EU migration, in relation to the main source and receiving locations, as derived from the literature reviewed in the paper (Source: OPENspace). |
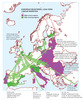 |
Figure 6:
Map showing the expected secondary migration flows in the EU in relation to the main source and receiving locations, as derived from the literature reviewed in the paper. (Source: OPENspace). |
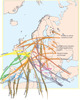 |
Figure 7:
Map showing anticipated migration flows from outside the EU and their main destinations, as derived from the literature reviewed in the paper. (Source: OPENspace). |
 |
Figure 8:
The spatial pattern of land use types according to the model arising from migration processes at NUTSx (Source: OPENspace). |
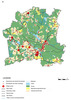 |
Figure 9:
Map showing the land abandonment in Dzerbene pagast (rural municipality), Latvia (Source: Simon Bell). |
 |
Figure 10:
Some examples of the results of depopulation and land abandonment in Latvia: a) a field no longer cultivated, becoming colonised by trees; b) ruined buildings following the dismantling of the collective farm system; c) an old farmhouse which has collapsed following abandonment. All examples from Dzerbene pagast, Latvia (Source: Simon Bell). |
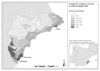 |
Figure 11:
A map showing the density of retired people along the coast of the Alicante region in Spain (Source: Zasada et al., 2010). |
 |
Figure 12:
Some examples of development and associated features resulting from international retirement migration in the Alicante region of Spain: a) an extra-urban “urbanización” housing development surrounded by traditional landscape elements; b) an “urbanización” next to a highly manicured and irrigated golf course; c) an example of highly manicured and water intensive non-native ornamental planting (Source: Ingo Zasada). |
 |
Figure 13:
Some examples of residential areas occupied by migrants from Cape Verde in Lisbon, Portugal: a & b) a poor area of informally developed and unplanned housing at Cova da Moura, Lisbon; c) social housing erected for poor immigrants near Cova da Moura. (Source: Eva Silveirinha de Oliveira). |

